Just in case you are looking for it all in one place, and easily copy and pastable (like I was. . .and did not find) check out the Leg and foot muscles, and their origins, insertions and actions. And to start us off:
Gastocnemius
Action: Flex the knee, plantar flex the ankle
Origin: Condyles of the femur, posterior surfaces
 Insertion: Calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
Insertion: Calcaneus via calcaneal tendonSoleus
Action: Plantar flex the ankle
Origin: Soleal line; proximal, posterior surface of tibia and posterior aspect of head of fibula
Insertion: Calcaneus bia calcaneal tendon
Plantaris
 Action: Weak plantar flexion of the ankle, weak flexion of the knee
Action: Weak plantar flexion of the ankle, weak flexion of the kneeOrigin: Lateral supracondylar line of femur
Insertion: Calcaneus via calcaneal tendon

Popliteus
Action: Medially rotate the flexed knee, flex the knee
Origin: Lateral condyle of the femur
Insertion: Proximal, posterior aspect of tibia
Peroneus Longus
 Action: Evert the foot, assist to plantar flex the ankle
Action: Evert the foot, assist to plantar flex the ankleOrigin: Head of fibula and proximal two-thirds of lateral fibula
Insertion: Base of the first metatarsal and medial cuneiform
Peroneus Brevis
Action: Evert the foot, assist to plantar flex the ankle
Origin: Distal two-thirds of lateral fibula
Insertion: Tuberosity of fifth metatarsal
 Extensors of the Ankle and Toes
Extensors of the Ankle and ToesTibialis Anterior
Action: Invert the foot, Dorsiflex the ankle
Origin: Lateral condyle of tibia; proximal, lateral surface of tibia and interosseous membrane
Insertion: Medial cuneiform and base of the first metatarsal
Extensor Digitorum Longus
Action:
Origin: Lateral condyle of tibia; proximal, anterior shaft of fibula and interosseous membrane
Insertion: Middle and distal phalanges of second through fifth toes
Action:
- Extend the first toe
- Dorsiflex the ankle
- Invert the foot
Origin: Middle, anterior surface of fibula and interosseous membrane
Insertion: Distal phalanx of first toe
Flexors of the Ankle and Toes
 Tibialis posterior
Tibialis posteriorAction: Invert foot and plantar flex ankle
Origin: Proximal post. shaft of tibia, proximal fibula and interosseous membrane
Insertion: Navicular cuneiforms, cuboid and bases of second through fourth metatarsals
Flexor digitorium longus
Action: Flex second through fifth toes, invert foot and weak plantar flexion of ankle
Origin: Middle post. surface of tibia
Insertion: Distal phalanges of second through fifth toes
Flexor Hallucis Longus
 Action: Flexfirst toe, invert foot and weak plantar flexion of ankle
Action: Flexfirst toe, invert foot and weak plantar flexion of ankleOrigin: Middle half of post. fibula
Insertion: Distal phalanges of first toe
Extensor digitorum longus
Action: Extends toes and extends foot at ankle
Origin:Upper two thirds of anterior shaft of fibula, interosseous membrane and superior tibiofibular joint
Insertion: Extensor expansion of lateral four toes
 Extensor Digitorum Brevis
Extensor Digitorum BrevisAction: Extend second through fourth toes
Origin: Calcaneus
Insertion: Second through fourth toes via extensor digitorum longus tendons
Flexor Digitorum Brevis
Action: Flex middle phalanges of second through fifth toes
Origin: Calcaneus
Insertion: Middle phalanges of second through fifth toes

 Abductor Hallucis
Abductor HallucisAction: Abduct first toe and assist to flex first toe
Origin: Calcaneus
Insertion: Proximal phalange of first toe
Abductor Digiti Minimi
Action: Flex fifth toe and assist to abduct fifth toe
Origin: Calcaneus
Origin: Calcaneus
Insertion: Proximal phalange of first toe
Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Action: Flex first toe
Insertion: Med. and lat. sides of base of proximal phalange of first toe
Adductor Hallucis
Action: Adduct first toe and assist to maintain transverse arch of foot
Origin: Oblique head- Bases of second through fourth metatarsals
Transverse head- Platar ligament of third through fifth metotarsophalangeal joints
Insertion: Lat. surface of base of proximal phalange os first toe and lateral sesamoid bone
Abductor Hallucis
Action: Flexes and abducts big toe. Supports medial longitudinal arch
Origin: Medial process of posterior calcaneal tuberosity & flexor retinaculum
Insertion: Medial aspect of base of proximal phalanx of big toe via medial sesamoid

Flexor digiti minimi brevis
Action: Flexes metatarsophalangeal joint of little toe
Origin: Base of 5th metatarsal and sheath of peroneus longus
Insertion: Lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of little toe
Quadratus Plantae
Action: Assist flexor digitorum longus to flex second through fifth toes
Origin: Platar surface of calcaneus
Lumbricals
Action: Flex proximal phalanges of second through fifth toes at metatarsophalangeal joints and extend middle and distal phalanges of second through fifth toes and interphalangeal joints
Origin: Tendons of flexor digitorum longus
Insertion: Bases of proximal Phalanges of second through fifth toes and expansions of extensor digitorum longus tendons
Origin: Bases of third through fifth metatarsals
Insertion: Medial surfaces of proximal phalanges of third through fifth toes
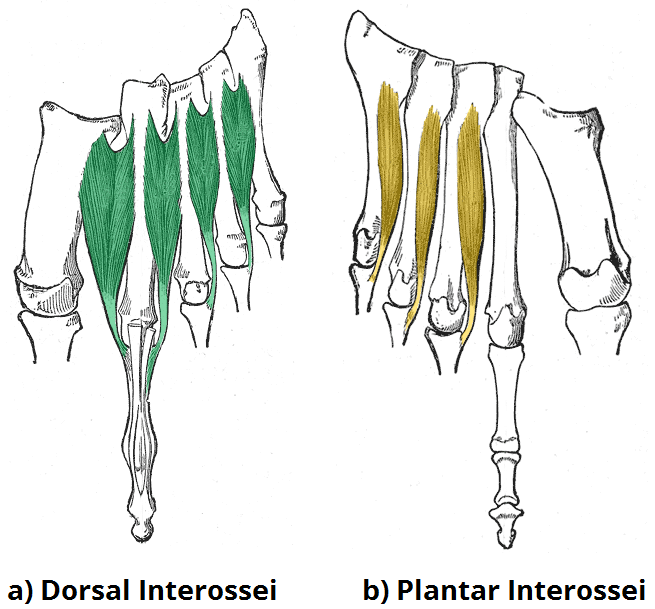
Dorsal Interossei
Action: Abduct and flex second through fourth toes
Origin: Shafts of first through fourth metatarsals
Insertion: First- Medial surface of proximal phalange of second toe
Second through fourth- Lateral surfaces of proximal phalange of second through fourth toes
I hope this was a help to you as just making it has been to me. Please comment below if I missed anything or said something wrong, as I simply am copying others work here, and don't know this stuff myself yet.